Introduction
Experts foresee that quantum computing is the next big tech for 2023 and we cannot ignore it. This article sheds light on quantum computing and its rising importance in various application domains. Then it focuses on the important application of quantum computing in banking and finance. The article concludes with road ahead for Arab banks to embrace quantum computing.
RISE OF QUANTUM COMPUTING
In the Economist World Ahead 2023, Jack Hidary, predicated that quantum technologies will have a profound impact on our society from banking to clean energy. Technologies, which include communications, computing, quantum sensing and simulation, will bring many benefits and make a dramatic shift in the global cyber-security architecture.
Quantum computers are still under development. But as they become more powerful and more reliable, they will pose a threat to how we transmit and store confidential data including bank transactions, sensitive government information and intellectual property. That is because unlike existing computers, quantum computers will be able to crack the encryption systems that provide secure data communication and storage, and underpin the global economy.
What Is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a process that uses the laws of quantum mechanics to solve problems too large or complex for traditional computers. Quantum computers rely on qubits to run and solve multidimensional quantum algorithms.
Quantum computing is vastly different from classical computing. Quantum computing solves mathematical problems and runs quantum models using the tenets of quantum theory. Some of the quantum systems used include photosynthesis, superconductivity and complex molecular formations.
Quantum computers process information in a fundamentally different way than classical computers. Traditional computers operate on binary bits but quantum computers transmit information via qubits. The qubit’s ability to remain in superposition is the heart of quantum’s potential for exponentially greater computational power.
Quantum computers utilize a variety of algorithms to conduct measurements and observations. These algorithms are input by a user, the computer then creates a multidimensional space where patterns and individual data points are housed.
Quantum bits, or qubits, are the basic unit of information in quantum computing. Qubits use superposition to be in multiple states at one time. Binary bits can only represent 0 or 1. Qubits can be 0 or 1, as well as any part of 0 and 1 in superposition of both states. Qubits can be made from trapped ions, photons, artificial or real atoms or quasiparticles, while binary bits are often silicon-based chips.
Quantum superposition occurs when quantum particles are a combination of all possible states. The particles continue to fluctuate and move while the quantum computer measures and observes each particle.
Quantum particles are able to correspond measurements with one another, and when they are engaged in this state, it’s called entanglement. During entanglement, measurements from one qubit can be used to reach conclusions about other units. Entanglement helps quantum computers solve larger problems and calculate bigger stores of data and information.
As qubits experience superposition, they can also naturally experience quantum interference. This interference is the probability of qubits collapsing one way or another. Because of the possibility of interference, quantum computers work to reduce it and ensure accurate results.
investment in QUANTUM COMPUTING
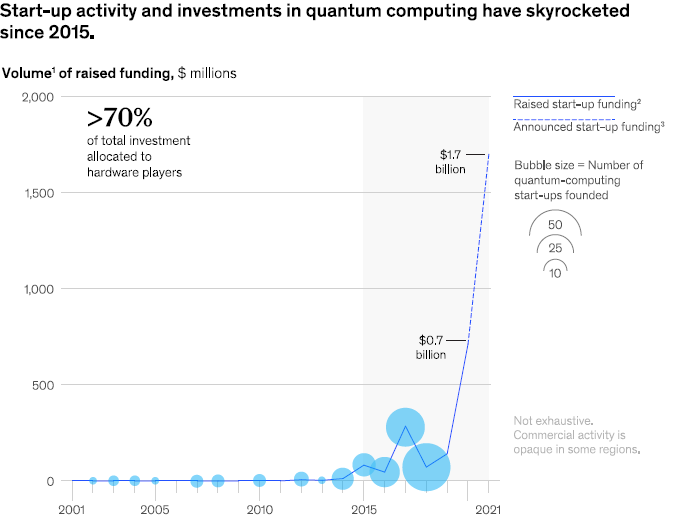
Quantum technologies is rapidly advancing toward commercial viability. Big investment is made in this emerging technology, and there is a rising number of quantum-computing start-ups.
Major technology companies continue to develop their quantum capabilities such as Alibaba, Amazon, IBM, Google, and Microsoft. For instance, Microsoft have already launched commercial quantum-computing cloud services.
McKinskey research indicates that the value at stake for quantum-computing players is nearly $80 billion. Because quantum computing is still a young field, the majority of funding for basic research in the area still comes from public sources.
Quantum Computing Hardware
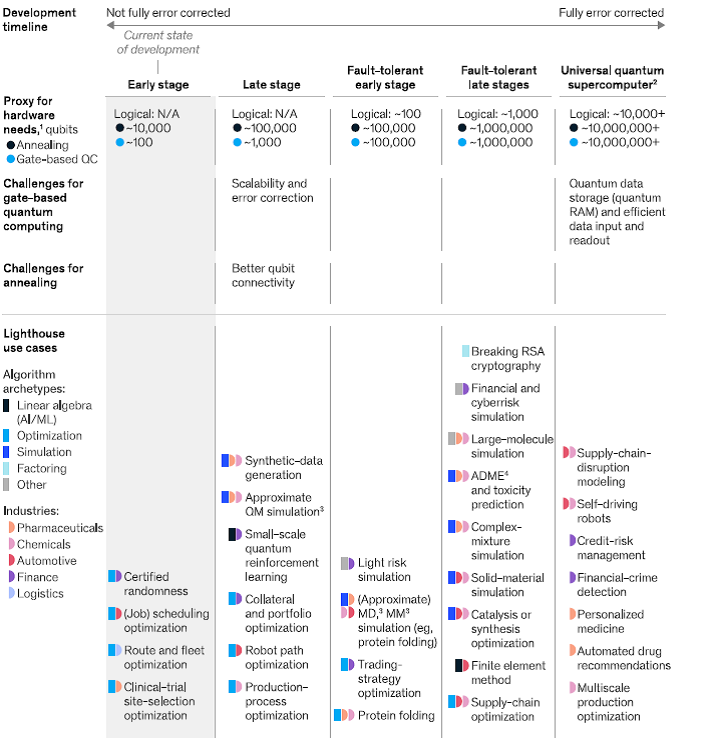
Multiple quantum-computing hardware platforms are under development. The most important milestone will be the achievement of fully error-corrected, fault-tolerant quantum computing hardware.
Big tech manufacturers have announced plans to have fault-tolerant quantum-computing hardware by 2030. Technology companies like IBM, Microsoft and Intel have developed quantum simulators and processors that can be accessed through avenues like purchase or special memberships. There are also a variety of open-source quantum toolkits on the market that can be accessed online, like GitHub.
The physical build of a true quantum computer consists mainly of three parts. The first part is a traditional computer and infrastructure that runs programming and sends instructions to the qubits. The second part is a method to transfer signals from the computer to the qubits. The third part is the storage unit for the qubits. This storage unit for qubits must be able to stabilize the qubits and certain needs or requirements have to be met. These can range from needing to be near zero degrees or the housing of a vacuum chamber.
Quantum Computing Software
Quantum computing requires a new programming paradigm. Cloud-based quantum-computing services can create outsize rewards to those who control them. Most providers of cloud-computing services now offer access to quantum computers on their platforms, which allows potential users to experiment with the technology. Since personal or mobile quantum computing is unlikely this decade, the cloud may be the main way for early users to experience the technology until the larger ecosystem matures.
Peneration of QUANTUM COMPUTING in various industries
Most applications of quantum computing fit into four categories: quantum simulation, quantum linear algebra for Artificial Intelligence AI and machine learning, quantum optimization and search, and quantum factorization.
Quantum computing penetrated various industries so far including:
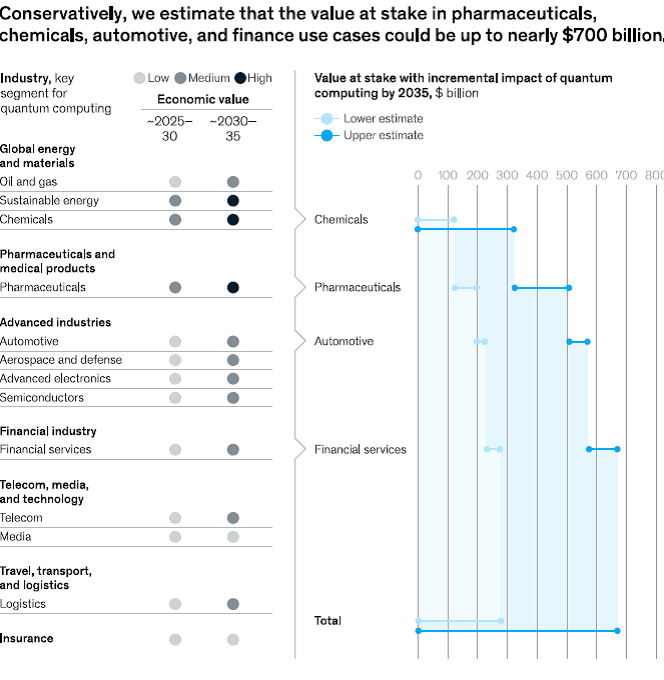
- Financial industry: The most promising application of quantum computing in finance are in portfolio and risk management. For example, efficiently quantum-optimized loan portfolios that focus on collateral could allow lenders to improve their offerings, possibly lowering interest rates and freeing up capital.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the research and development of molecular structures in the biopharmaceuticals industry as well as provide value in production and further down the value chain. Quantum computing could make Research and Development (R&D) dramatically faster and more targeted and precise by making target identification, drug design, and toxicity testing less dependent on trial and error and therefore more efficient.
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry can benefit from quantum computing in its Research and Development (R&D), product design, supply-chain management, production, and mobility and traffic management.
- Global energy and materials industry: Quantum computing can better help in the transition to clean and sustainable energy.
- Advanced industries: Quantum computing can better support research and development in advanced industries such as aerospace and defence, advanced electronics, and semiconductors.
- Telecom, media, and technology industries: Quantum computing can help telecom, media, and technology industries in better harnessing the power of data.
QUANTUM COMPUTING IN BANKING AND FINANCE
According to Insider Intelligence, many banks have started working on quantum computing projects that could one day become part of their normal operations. The speed-up in computing time is the main driver to use quantum computing in financial services. Quantum computing financial applications include:
- Portfolio optimization: Quantum computers can run Monte Carlo simulations in impressive time. These simulations analyse risk-and-return trade-offs on combinations of investments to optimize a portfolio based on a customer’s goals and risk tolerance.
- Derivatives pricing: This is a complex undertaking because the price of derivative instruments depends on the price of an underlying asset. Variable factors like counterparty risk, time to expiration, and interest rates all influence the price. Quantum computing can simulate a large number of scenarios in seconds to determine an appropriate price.
- Cybersecurity: Quantum computing would enable fraudsters and bad actors to build a program that could break down the cryptography of a cybersecurity program in seconds. But the technology could be used in useful ways to create an unbreakable defence that no malicious actor could get through.
- Daily practices: Quantum computing offers a competitive advantage. Banks and financial institutions that are able to implement quantum computing in their daily practices could be ahead of their competitors. They could reduce the processing time for many daily tasks to mere seconds.
Top 10 quantum computing applications in 2023
According to Analytics Insights, the top 10 applications of quantum computing in 2023 are:
- Quantum cryptography: One of the most unique applications of quantum computing is quantum cryptography which majorly focuses on the key distribution part of a cryptosystem.
- Drug design and development: quantum computing can be an effective way of understanding drugs and their reactions to humans thereby saving a lot of money and time for drug companies.
- Financial modelling: The technique of ‘Monte Carlo’ simulations is continually being run on conventional computers. The problem with this is that it consumes an enormous amount of computer time. However, by applying quantum technology to perform these massive and complex calculations, companies can not only improve the quality of the solutions but also reduce the time to develop them.
- Weather Forecasting: Quantum computing can crunch vast amounts of data, in a short period. Quantum computing could enhance weather system modelling by allowing scientists to predict the changing weather patterns in no time and with excellent accuracy.
- Advertising: Quantum computing can help advertising companies reach a wider range of people.
- Traffic flow management: With quantum computing, one can tackle the issue of traffic, by optimizing traffic flow itself. Quantum computers can find the optimal route for a select number of cars and possible routes to take.
- Better mobile network coverage: Quantum computers can help find the optimal satellite coverage position required.
- Cybersecurity: Quantum computing with the help of machine learning can help in developing various techniques to combat cybersecurity threats.
- Gaming: Quantum hardware can compute faster than the current best computers. This improves gaming experience because quantum computer algorithms work very differently from classical ones.
- Computational chemistry: The ability for quantum computers to focus on the existence of both 1 and 0 simultaneously could provide immense power to the machine to successfully map the molecules. This in turn opens opportunities for pharmaceutical research.
CHALLENGES FACING QUANTUM COMPUTING
The main challenge of implementing quantum computing is the maturity of the technology. Quantum computers are generally designed to solve very specific problems, and they are sensitive to any kind of disturbance, like noise and dust.
Various challenges may face banks in seamlessly implementing quantum computing technology because quantum computers are still in early stages. In order to address these challenges banks can enter in partnerships with quantum computing financial technology firms (quantum fintechs).
Banks also face the challenges of tight regulations. New regulation will be needed to control and supervise the use of quantum computing in banks and financial institutions.
Road ahead for arab banks to embrace quantum computing
Worldwide spending on quantum computing is expected to reach $630 million by 2027 and $2.2 billion by 2030, according to Inside Quantum Technology.
Quantum computing ecosystem and its use in various application domains will create significant value for industries.
Arab banks should prepare to embrace quantum computing as the technology matures.
Technology experts foresee that until about 2030, quantum-computing applications will have a hybrid operating model that is a blend of quantum and conventional high-performance computing.
Various key factors will determine the technology’s path to commercialization. These factors are:
- Funding
- Accessibility
- Standardization
- Collaboration
- Partnerships
- Expertise
- Digital infrastructure
Below are suggested steps for Arab banks to prepare for embracing quantum computing:
- Step #1. Follow up latest developments in the field of quantum-computing and its application.
- Step #2. Collaborate with industry entities and fintech to develop quantum computing based financial services.
- Step #3. Assess risks and opportunities offered by quantum computing for banks and financial institutions.
- Step #4. Partner with quantum computing developers to facilitate access to knowledge and talent.
- Step #5. Invest in quantum-computing hardware and software.
- Step #6. Build in-house expertise in quantum-computing.
- Step #7. Develop a bank digital infrastructure that can meet the basic operating demands of quantum computing.
- Step #8. Develop a strategy to embrace quantum computing.



