BY DR SOHA MAAD
Introduction
The world is looking at crypto currency as a safe haven from inflation because it is well calculated and managed and may not cause inflation. Excessive printing of fiat money by government is one of the main causes of inflation, however by adopting central bank digital currency the inflation problem may not arise. In this article we explore various views about the relationship between crypto currency and inflation with the aim to identify a pattern of relationship over time. Experts’ views from world organizations, companies, academia, and financial information sources are considered including International Monetary Fund (IMF), Binance, Elsevier Economics Letters, Investopedia, Coindesk, CNBC, Coin Telegraph, and Financial Post. The article concludes with recommendation to Arab banks and authorities to build expertise in crypto currency and to develop a unified central bank digital currency that can help in addressing the inflation challenge caused by excessive printing of fiat money. Islamic banks can play a key role in helping to keep the inflation down and supporting the Zero Inflation target advocated by the International Monetary Fund.
Rising world inflation
Lately, inflation has been a persistent rather than a transitory phenomenon. Largely driven by the global response to the pandemic, financial markets are seeing a steady rise in inflation rates worldwide.
Inflation is the process by which the decreasing value of a currency leads to an increase in the price of goods and services over time. In other words, inflation is caused by governments printing more money than is needed.
Inflation rose significantly in 2020 as governments worldwide were forced to inject trillions of dollars to help stimulate a stagnating economy caused by the coronavirus pandemic. But now that economies are reopening and consumer spending is picking up, governments face a difficult task ahead.
According to the famous economist John Maynard Keynes, inflation is not a horrible thing in some situations, and can actually boost the economy and create new jobs during downtimes. Overall, a low inflation rate stimulates spending, investment and borrowing. On the other hand, when inflation spins out of control, it leads to hyperinflation, causing the price of goods and services to rapidly increase while wages stagnate, currency purchase power decreases and living costs become more expensive.
Higher inflation erodes the value of the saved money and lower inflation slows the economy as a whole.
Economists disagree about the causes of the current rising world inflation described as the worst in decades. Some people point their fingers at the United States Federal Reserve for printing too much money, which in turn was used to stimulate the economy and handle the pandemic. Others say that the United States Federal Reserve is not the one to blame. Supply shortages caused by lockdowns were the main problem.
Economists think that a moderate inflation is helpful to keep people buying, thereby stimulating the economy. But in times of economic crisis, like war and coronavirus pandemic, inflation can get out of hand.
Cryptocurrency trend
According to the Guardian latest news in 29 June 2022, there is crypto crisis and digital currencies are going from boom to collapse. with bitcoin falling below the $20,000 mark in June 2022, far below its peak of nearly $69,000, which it hit in November 2021.
The fall has been sharp and spectacular. An overall market that was estimated to be worth more than $3tn barely by the end of 2021 is now worth less than $1tn.
According to New York Times news, the price of Bitcoin plunged to its lowest point since 2020. Coinbase, the large cryptocurrency exchange, tanked in value. A cryptocurrency that promoted itself as a stable means of exchange collapsed. And more than $300 billion was wiped out by a crash in cryptocurrency prices and the crypto world went into a full meltdown in March 2022.
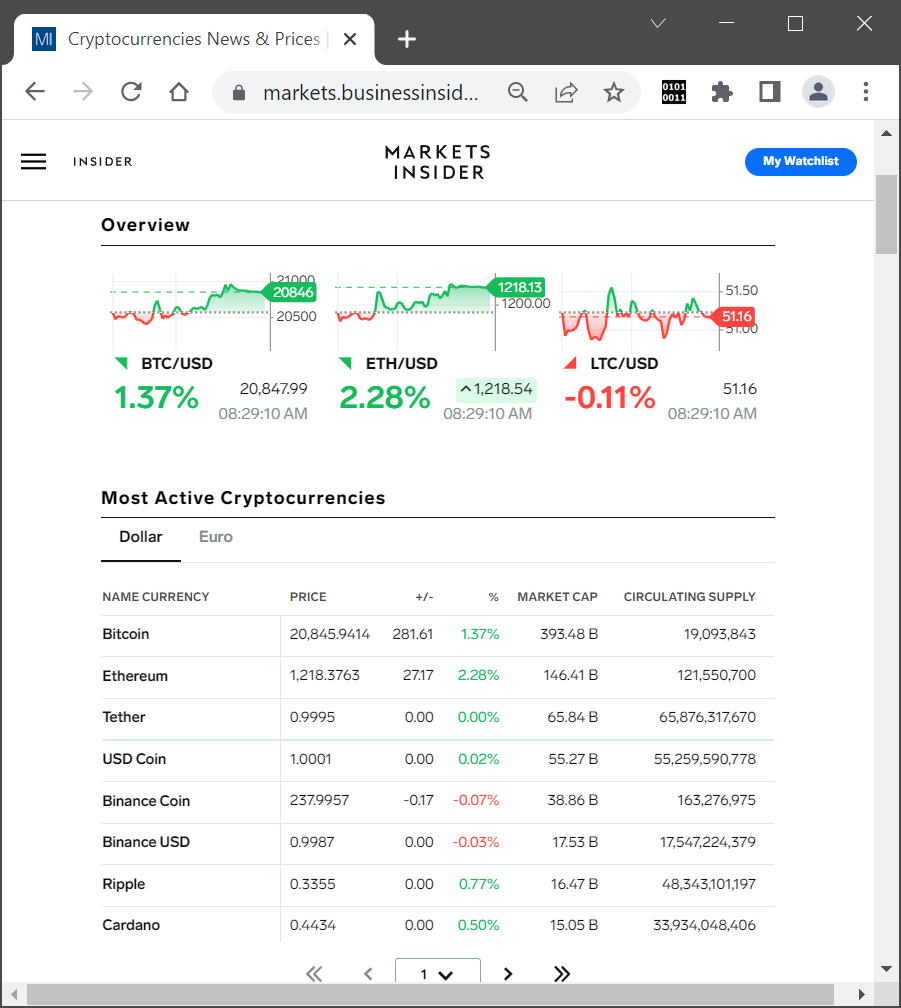
(Source: Markets Insider https://markets.businessinsider.com/cryptocurrencies)
The relationship between Cryptocurrencies And Inflation
Latest news update reveals cryptocurrencies and inflation are going in opposite direction, while inflation is rising the cryptocurrency market is slumping.
Binance presents a complete analysis of inflation and its relationship with cryptocurrency. Binance is an online exchange where users can trade cryptocurrencies. It supports most commonly traded cryptocurrencies. Binance provides a crypto wallet for traders to store their electronic funds. The exchange also has supporting services for users to earn interest or transact using cryptocurrencies.
Below is a highlight of the key points raised in Binance analysis of the role of crypto currencies and bitcoin during inflation.
Since inflation has been a constant threat to the value stored in fiat, people often protect themselves by investing in assets that maintain their value over time. Historically, gold has been used as a hedge against inflation, but now crypto has become a more popular alternative over recent years. Use of cryptocurrency during inflation include:
Hedging against inflation
Bitcoin is fundamentally a deflationary asset, which is why citizens of countries with unstable fiat currencies are increasingly using it as a store of value to protect against hyperinflation and rising costs of everyday goods and services. Unlike fiat, crypto cannot be manipulated to the same extent by changing interest rates and increased money printing. Most importantly, Bitcoin’s supply will never exceed 21 million which makes it an attractive store of value that is resistant to inflation. While Bitcoin has surged in popularity over the past year, the crypto market’s volatile nature continues to be a polarizing topic.
Stablecoin Alternative
Cryptocurrencies often experience sudden price movements, which for many, makes them an unattractive store of value. Investors hesitant about crypto’s volatile nature, can consider using secured, fiat-backed stablecoins.
The Link Between Bitcoin and Inflation
Coindesk analysis by Robert Stevens, revealed that some investors have flocked to bitcoin in order to protect their wealth from the impact of rampant inflation.
CoinDesk is Bitcoin, Ethereum, Crypto news and price data. It is leader in cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP, blockchain, Decentralized Finance DeFi, digital finance and Web 3.0 news.
Cryptocurrency is often considered an inflation-resistant asset, and is often seen as an asset class that is uncorrelated with real-world assets. However, cryptocurrencies are unique and some are inflationary by design.
Crypto advocates think that allowing central bankers to influence the economy through monetary policies, namely quantitative easing, leads to disaster.
Crypto advocates often say that cryptocurrencies like bitcoin (BTC) are resistant to the incompetence of central bankers and governments because they are decentralized, and cannot be shut down. Another reason is that bitcoin’s issuance is determined by code.
While more bitcoin enters circulation over time, the rate at which new bitcoin is issued to miners is determined by the Bitcoin protocol. The supply is capped, and supplies of new coins are estimated around the year. And unlike central banks, whose economists must respond to market events, the Bitcoin blockchain runs like clockwork.
Approximately every four years, the protocol cuts the issuance of new bitcoin by half, known as the “halving”.
Bitcoin’s fixed supply has led some fans to consider it akin to “digital gold” which is inflation-resistant asset. Stores of value assets stand the test of time because they are uncorrelated with other assets and are resistant to entities that interfere with the market.
In the past few years, bitcoin has tracked the United States stock market, which performs well when the economy is stimulated and stutters when spending decreases.
However, not all cryptocurrencies work like bitcoin. Some cryptocurrencies are deflationary meaning that the supply decreases over time, designed to increase the value of the coin over time if the demand remained the same.
Other cryptocurrencies have dynamic supplies and some tokens, like non-fungible tokens (NFTs), are one of a kind.
Time-scale analysis of RELATION BETWEEN Inflation and crypto
Academic research by Thomas Conlona (et al), published in Elsevier Economics Letters, attempted to identify the time-series relation between cryptocurrency prices and forward inflation expectations. Using wavelet time-scale techniques, a positive link between cryptocurrencies and forward inflation rates is identified, focused on a brief period surrounding the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. This coincides with a rapid and synchronized decrease in cryptocurrency prices and forward inflation expectations, followed by a swift recovery to pre-crisis levels. Outside of the crisis period, there was no clear evidence of any inflation hedging capacity of Bitcoin or Ethereum during times of increasing forward inflation expectations.
During previous occasions of high inflation, investors attempted to preserve their purchasing power by investing in assets such as gold, property and stocks. The recent addition of cryptocurrencies as an investment option has added a possible new alternative inflation hedge. Empirical findings suggest that cryptocurrencies do not hedge against increases in forward inflation expectations, but instead may derive price-related information from factors common to forward inflation expectations during times of crisis.
These findings add to the mounting questions over the role of cryptocurrencies as a financial asset. While a transitory link between cryptocurrencies and forward inflation expectations is evident, the absence of consistent hedging properties may be a cause for alarm as investors attempt to find storage of value outside of traditional mechanisms. Such desperation to maintain wealth within ultra-risky assets ripe with criminality will be of concern for policy-makers and regulators alike.
ELECTRONIC MONEY STANDARD AND ZERO INFLATION TARGET
The International Monetary Fund IMF Analysis series by Ruchir Agarwal and Miles Kimball published in April 2022, reflects about the future of inflation and discusses how a move to an electronic money standard can lower the inflation target toward zero.
A world with lower inflation (and even zero inflation) and no persistent recessions may sound like a dream, but it is possible by transitioning to an “electronic money standard.” Breaking the zero lower bound implies that the optimal rate of inflation will be lower than in the presence of the lower bound. This will empower central banks to quickly restore full employment and, over the medium term, possibly move toward targeting full price stability with zero inflation.
Electronic money is money that is instantiated as an entry in a bank’s computer. This include the use of checks, credit cards, and debit cards in transactions. Given this definition of electronic money, the alternative to the “paper standard” can be called the “electronic money standard”.
A zero lower bound can be broken through a combination of adopting or strengthening an electronic money standard in which electronic money is the unit of account and implementing a time-varying interest rate (or more generally, rate of return) on paper currency (cash). Then, as the interest rate on cash moves in line with the official policy rates, there is no arbitrage between cash and money in the bank. Operationally this can be done while remaining quite close to the current monetary system, but there are several legal, communication, and political challenges to a transition to such an electronic money standard.
An essential element of an electronic money standard is that it does not require the elimination of paper currency to enable deep negative rates. It is enough to modify paper currency policy. Any arbitrage between cash and electronic money is at the expense of a central bank’s balance sheet.
Moving from a paper standard to an electronic money standard can empower monetary policy to cut interest rates as much as needed for economic stimulus during recessions while enabling a gradual shift to zero inflation target as depicted in Figure 3.
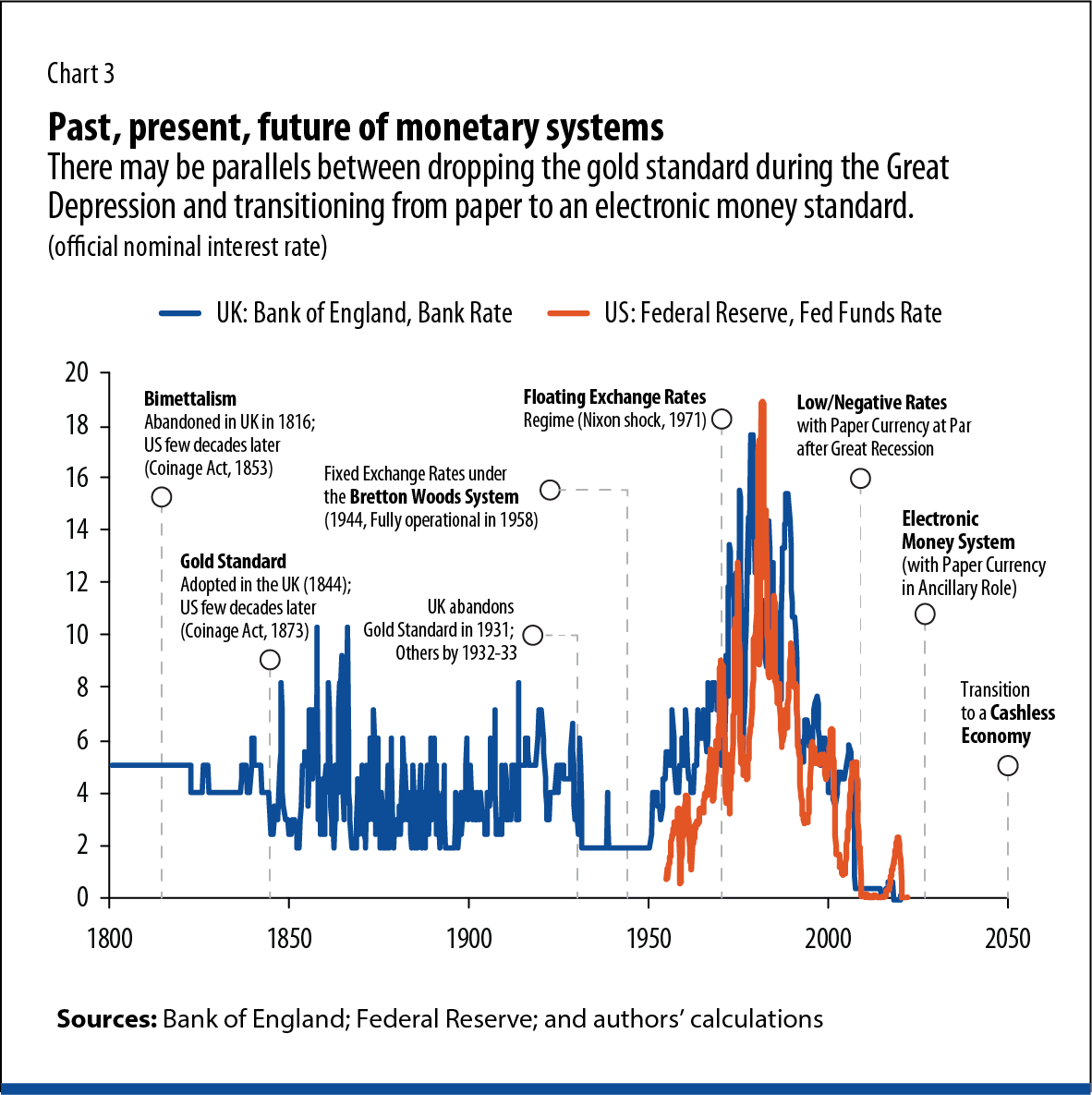
Future monetary system
The transition to an electronic standard with a Zero Inflation target will benefit from the use of several complementary tools:
- Subsidies:The interest-on-reserves formula can be used to subsidize zero rates on small deposit accounts.
- Macroprudential measures: These include raising capital requirements and imposing stricter amortization requirements.
- Measures to overcome downward wage stickiness, particularly by creating incentives for firms to pay a substantial fraction of compensation in the form of bonuses that can vary from year to year.
Central bank DIGITAL CURRENCY potential to FIX INFLATION
The hinder Business Line opinion of Guido Cozzi affirms that central bank digital currency (CBDC) can fix the inflation problem.
Guido Cozzi opinion is that a good way to arrest the fall in the value of a nation local currency and contain the nation fiscal deficit is through the use of digital currency. Initially faced with the popularity of private cryptocurrencies, central banks are designing central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) that will completely revolutionise payment systems. China has begun experimenting with its digital yuan, the European Central Bank is designing the digital euro, and The United States Federal Reserve is thinking of developing its digital dollars.
Policymakers around the world are faced with a dilemma on whether to control inflation or support growth. In the context of Covid-19, the onus fell on the government to take up deficit financing to keep the economy going. This activity was supported by central banks, which lent easy money through quantitative easing, thereby increasing money supply and lowering interest rates.
The Russia-Ukraine war has changed the global economic scenario. Higher commodity and oil prices coupled with supply-side glitches raised inflation. For India, which is a major importer of crude, consumer price inflation is inching towards the 8 per cent mark. The inflation scenario in the US is no different, recording 8.3 per cent in April, among the highest levels in four decades.
Higher inflation expectations on account of the war, triggering higher commodity and fuel prices, has led to a fall in consumer purchasing power. This could lead to industry leaders not willing to invest, causing a further fall in employment generation and growth.
The present inflationary factor has more to do with the supply-side shock. In such circumstances, it does not make sense to follow tight monetary policy to control inflation. It would seem that central bankers are resorting to quantitative tightening to control the value of the exchange rate.
Financial post analysis by Ethan Lou suggests that central bank digital currency could be an inflation-fighter’s best friend. A central bank digital currency theoretically allows for micro-targeting with real-time feedback.
CRYPTO vulnerability to inflation and taxes and market trends
Investopedia analysis by Nathan Reiff, reveals that cryptocurrencies are affected by inflation, taxes, and market Trends. Top cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and BNB may be more susceptible to external market factors than some crypto enthusiasts believe. These and other major tokens fell sharply in the first two weeks of April 2022, with the broader crypto market losing almost $400 billion of value during that time. Analysts view that a “disaster” in the financial markets could send crypto prices plunging even further.
While Bitcoin has moved above and below a price threshold of $40,000 throughout most of 2022, the latest price drop is a reminder to investors that decentralized digital tokens may still react strongly to factors such as inflation, taxes, and overall market performance.
The recent slump in cryptocurrency price levels may also be due in part to tax season.
Federal Reserve increase of interest rates and borrowing costs may be felt most prominently in traditionally riskier areas like cryptocurrency. Rising bond yields could also minimize excess return that investors could achieve from cryptocurrencies relative to safer bets like bonds. Combined with persistent inflation and other large-scale economic concerns, this shift may cause investors to turn away from cryptocurrencies to safer alternatives. This could be reflected in the price level of digital tokens for those who continue to trade in this space.
WAY FORWARD FOR ARAB BANKS AND AUTHORITIES
This article reveals that cryptocurrencies can play a major role during inflation. Below, we suggest some recommendations to Arab banks and authorities to leverage the potential benefits of crypto currencies in addressing and controlling the rising inflation problem:
Recommendation #1. Building expertise
Arab banks and authorities should build expertise in developing crypto currency tools and technologies.
Recommendation #2. Developing a unified central bank digital currency
Central Banks in Arab countries should collaborate to develop a a unified central bank digital currency that can help in addressing the inflation challenge caused by excessive printing of fiat money.
Recommendation #3. Important role for Islamic Banks in meeting Zero Inflation target
Islamic banks can play a key role in helping to keep the inflation down and supporting the Zero Inflation target advocated by the International Monetary Fund.
Recommendation #4. Transition to electronic money standard
As advocated by the International Monetary Fund, a transition to an electronic money standard holds the dual promise of providing monetary policy firepower to restore full employment quickly while targeting full price stability with zero inflation.


